The most important device required for this software to be usable, is a GNSS or RTK receiver. At this moment, all GNSS and RTK receivers with a NMEA0183 compatible data output are supported. It does not matter whether the NMEA0183 sentences are send over a serial port, USB port, Bluetooth connection or network connection. In this tutorial we talk about a "GNSS receiver", since the term "GPS receiver" is outdated, because most receivers these days are capable of using satellites from multiple constellations, like GLONASS, Galileo, Beidou and more.
The GNSS receiver is used to get position, elevation (ellipsoidal height and MSL height), course over ground, speed over ground and information on GNSS fix quality and precision. When using a RTK receiver in RTK fixed mode (correction data required), you should be able to get real time tide information as well, by using the high accuracy ellipsoidal height and a geoid model.
In order to connect a GNSS receiver, you need to have at least one serial port available (unless the receiver is connected via Bluetooth). If there is no port available, you can add a serial port by using an USB-to-serial converter or a NMEA0183 data combiner equipped with an USB port. Most RTK receivers also have the ability to connect them via Bluetooth - This also requires less cables running through your boat.

Trimble GNSS receivers and antenna's
When using an USB-to-serial converter, make sure it is connected to an USB port at the time you are going to configure the receiver. When using Bluetooth, make sure the device has been paired and connected to your computer. Because an USB-to-serial converter can cause minor (some brands major) delays (latency) in communications, we recommend to use a multi port serial adapter instead. Multi port serial adapters are available as PCI cards as well as PC-Cards for use in laptops.
In addition to NMEA0183 data over a serial device, Hydromagic is able to read NMEA0183 data over TCP/IP connections. This allows you to transfer data over, for instance an Ethernet or WiFi connection. Both TCP and UDP protocols are supported.
Video tutorial on how to configure a GNSS receiver connected via a serial port.
Hydromagic is able to decode the following NMEA0183 sentences transmitted by GNSS and RTK receivers:
| Sentence | Description |
|---|---|
| $GPGGA | Global Positioning System Fix Data, Ellipsoidal Height, Time and Position |
| $GPGLL | Geographic Position - Latitude and Longitude |
| $GPGMP | Projected Position - Easting, Northing and Elevation |
| $GPGSA | GNSS DOP and Active Satellites |
| $GPGSV | Satellites in view |
| $GPRMC | Recommended Minimum Navigation Information |
| $GPVTG | Track Made Good and Ground Speed |
| $GPZDA | GNSS Time |
| $PTNL,GGK | Trimble RTK positioning data and ellipsoidal height |
To add a NMEA0183 compatible device to the configuration, select "Preferences..." from the "Options" menu (or click the "Options" button in the toolbar) and select the "Devices" tab:
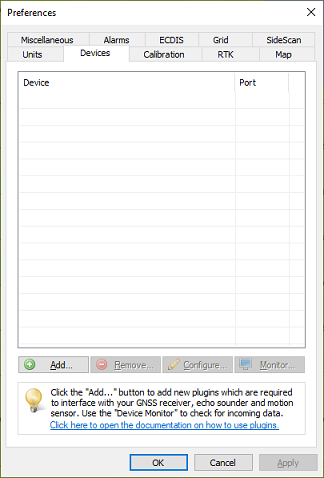
Select the "Devices" tab from the "Preferences" window.
In the devices tab, click the "Add..." button to load a NMEA0183 plugin. You can load a maximum of four (4) NMEA0183 plugins simultaneously. Next, select the first available "NMEA0183 plugin" in the "Select Device" dialog which appears after clicking the "Add..." button and click "OK" to show the plugin's configuration options.
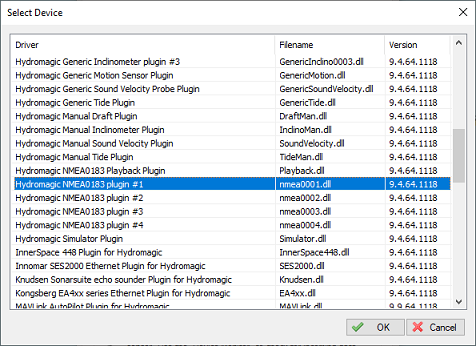
Select one of the "Hydromagic NMEA0183" plugins from the list and click "OK".
After the plugin has been loaded, a configuration dialog is displayed where you can pass the required information to the plugin.
The NMEA0183 plugin supports two types of connection types: serial and TCP/IP (networked). When a device is connected through an USB, Bluetooth or serial connection, you have to select the "Serial" option. In cases where the device is connected using an Ethernet cable or WiFi connection, you have to select the "TCP/IP" option from the "Connection Type" drop down box. When switching between the "Serial" and "TCP/IP" connection type, the function of the edit and selection boxes in the "Connection" section will change as shown in the screen shots above.
Use this drop down box to select the COMxx number of the serial port the device is connected to. This can be either a regular serial port, or a virtual serial port, which is used by USB-to-serial and Bluetooth adapters.
The default serial baud rate for NMEA0183 devices is 4800 bps. However, some hardware use other speeds (for instance, an AIS receiver will use 38400 bps). When configuring a GNSS or RTK receiver, the serial speed can sometimes deviate from the standard. 9600, 19200 and 38400 bps are mostly used on these devices.
You can leave this setting at it's default value (8,N,1). Devices that use NMEA0183 protocol with other settings are very rare.
Use the "Socket Type" drop down box to select the TCP/IP protocol used. Possible values are "TCP" and "UDP". Please refer to the hardware vendor or manual to see which options are supported. Most devices support both protocols.
The IP address of the device. This value is required only for TCP connections. For UDP connections, just provide a valid port number.
Enter the IP (TCP or UDP) port number the device is listening on here. For most wireless NMEA0183 devices, the port 10110 is used, which is the reserved port for NMEA0183.
Latency (sometimes called lag) is the time between a measurement has been made (for instance a position fix, or depth) and when the serial data is received by the application. If this value is known for a certain device, you can enter it here to get more accurate soundings, since the timestamps will be corrected when processing the raw data files.
Use this option to filter NMEA0183 sentences by talker ID.
It sometimes happens that both echo sounder and GNSS receiver are transmitting GNSS sentences, in this case you can either select the GNSS receiver or echosounder by specifying "GP", "GN" or "SD" in this field.
When using a multi constellation GNSS or RTK receiver, sometimes sentences are sent multiple times with different talker id's. For instance the data for GLONASS starts with '$GL', the data for GPS with '$GP', the data for Beidou with '$BD', etcetera. In these cases the combined data starts with '$GN' which stands for GNSS. To avoid duplicate data to be recorded, set the talker id to 'GN'.
$GPGGA,164343.00,3208.4408001,N,08048.1630431,W,4,08,1.21,-1.9491,M,-32.0232,M,1.0,0029*62 $GPGGA,164344.00,3208.4407115,N,08048.1629118,W,4,08,1.21,-1.9434,M,-32.0232,M,1.0,0029*67 $GPGGA,164345.00,3208.4406172,N,08048.1627910,W,4,08,1.21,-1.9208,M,-32.0232,M,1.0,0029*61Good: Only position data with 'GP' talker. No need to set filter.
$GNGGA,105338.00,0544.85881818,N,05356.94900227,W,4,17,0.6,5.383,M,-34.351,M,1.0,0004*6C $GNGGA,105339.00,0544.85795724,N,05356.95023683,W,4,17,0.6,5.370,M,-34.351,M,1.0,0004*68 $GNGGA,105340.00,0544.85695547,N,05356.95129001,W,4,17,0.6,5.391,M,-34.351,M,1.0,0004*68Good: Only position data with 'GN' talker. No need to set filter.
$GNGGA,060358.00,4039.8688766,N,02957.8791974,E,4,14,0.7,170.368,M,,,0.44,0000*38 $GPGGA,060358.00,4039.8688766,N,02957.8791974,E,4,08,0.7,170.368,M,,,0.44,0000*2B $GLGGA,060358.00,4039.8688766,N,02957.8791974,E,4,06,0.7,170.368,M,,,0.44,0000*39 $GNGGA,060359.00,4039.8684222,N,02957.8804691,E,4,14,0.7,170.373,M,,,0.43,0000*3A $GPGGA,060359.00,4039.8684222,N,02957.8804691,E,4,08,0.7,170.373,M,,,0.43,0000*29 $GLGGA,060359.00,4039.8684222,N,02957.8804691,E,4,06,0.7,170.373,M,,,0.43,0000*3BBad: Duplicate position data where only talker id differs. Set filter to 'GN'.
To select which NMEA0183 sentences will be decoded, and which ones will be ignored on this channel, click the "Select sentences..." button. The dialog that appears allows you to select which sentences are used. For most GNSS devices, selecting only the "GGA" sentence will suffice. If you choose to use the heading and speed calculated by the GNSS device, you should also select the "VTG" sentence.
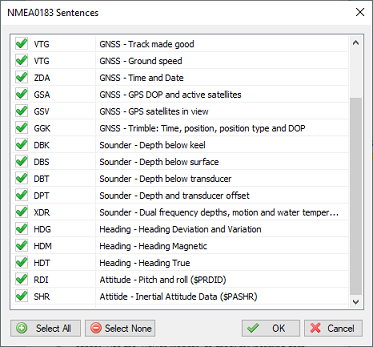
Select which NMEA0183 sentences are handled and which ones are ignored.
Some GNSS receivers use different sentences to send for instance the position data to the computer. To avoid duplicate data, the best is to configure the GNSS receiver to only output the most important sentences like GGA and VTG (starting from Hydromagic version 10, the GST sentence can be utilized as well). When it is not possible to change the output of the GNSS receiver, use the sentence settings to filter out unwanted duplicates. Find some examples of good and bad NMEA0183 outputs below:
$GPGGA,160359.00,1853.86383519,N,07010.07906236,W,4,11,0.8,212.022,M,-43.831,M,3.0,0000*7A $GPVTG,199.57,T,,M,0.16,N,0.30,K,D*3F $GPGGA,160400.00,1853.86379049,N,07010.07907892,W,4,11,0.8,212.012,M,-43.831,M,1.0,0000*70 $GPVTG,197.85,T,,M,0.18,N,0.33,K,D*33Good: No duplicate data here. No need to set filter, recommended NMEA0183 output settings for GNSS receivers.
$GPRMC,133652.90,A,4554.0847900,N,00608.6707562,E,001.970,171.5,061218,0.0,W,D*21 $GPVTG,171.540,T,171.540,M,1.970,N,3.648,K,D*20Bad: RMC already includes speed and heading, so no need for VTG here.
$GPGGA,121317.00,5301.5951868,N,00541.2031037,E,4,09,0.8,42.087,M,,,0.85,0020*19 $GPGGK,121317.00,031518,5301.5951868,N,00541.2031037,E,3,09,1.9,EHT42.087,M*7E $PTNL,GGK,121317.00,031518,5301.5951868,N,00541.2031037,E,3,09,1.7,EHT42.087,M*4D $GPGLL,5301.5951868,N,00541.2031037,E,121317.00,A,D*66Really bad: The same position is transferred using 4 sentences. Use GGA or GGK only.
The output rate is the number of times a particular NMEA0183 sentence is calculated and broadcast by the GNSS or RTK receiver. By default, for most receivers, the output rate is 1Hz which equals one time per second. Although Hydromagic works perfectly with an update rate of 1Hz, it is recommended to set it a little higher to improve accuracy. When for instance the echo sounder has an output rate of 10Hz, the Hydromagic software will calculate the positions for these soundings.
It is doing this by taking the position before and after the echo sounder ping. The more positions there are, the higher the accuracy. This is especially true when surveying at high speeds, or when there are sudden course or speed differences in your track. We recommend you to set the GNSS receiver at the same output rate as the echo sounder, or at least at the closest as possible value. How to set this value differs per GNSS or RTK receiver. Please contact your dealer or refer to the manual for more information.
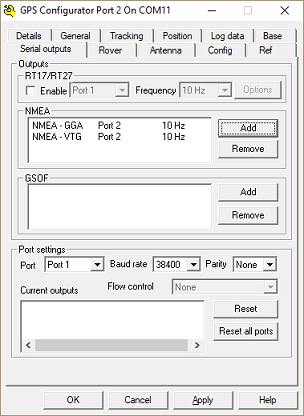
Modifying NMEA0183 serial output settings on a RTK receiver (Trimble)
When everything has been configured correctly, and the GNSS has been switched on and has a valid fix, the position fields in the "Navigation View" should have green values:
When no data is displayed, you can check whether data is coming in by using the "Communications Monitor": Open the preferences window by selecting "Preferences..." from the "Options" menu. In the window that appears, select the "Devices" tab. Next select the "Hydromagic NMEA0183 plugin" and click the "Monitor..." button. The communication monitor appears. When the monitor displays garbled data or no data at all, the serial port or serial speed setting might be incorrect.
When you encounter problems getting the serial port to receive data, we suggest you to have a look at our YouTube tutorial on troubleshooting serial communications using the puTTY software (free software).
Start the "Communications Monitor" to monitor incoming NMEA0183 data.